How Does Surrogacy Work in India?
Gestational Surrogacy in India has been a popular option for many intended parents from around the world due to its affordability, well-regulated process, and high-quality medical facilities. However, recent changes in the law have reshaped the surrogacy landscape. Understanding how surrogacy works in India is essential for intended parents who are considering this option for building their families.
This guide will walk you through the surrogacy process in India, including the legal framework, the steps involved, and the key factors you need to consider before embarking on a surrogacy journey.
- Book an online appointment: Get a free online consultation.
- Call\W:+91-8800481100 Email:neelam@ivfconceptions.com
We are a leading International Surrogacy Industry Expert with more than 15 years of global experience and expertise. Get in touch with us about affordable, reliable, and legal surrogacy options.
More Resources to Read:
Surrogacy Twins Cost: What to Expect
Disqualifications for Surrogacy For Surrogates: Key Factors
Cost of Surrogate Mother in India: A Complete Guide
Surrogates and Abortion: What to Know Before This Journey
Surrogacy in India: An Overview
Surrogacy is an arrangement in which a woman (the surrogate mother) carries and delivers a baby for another person or couple (the intended parents). This can be done through two types of surrogacy:
- Traditional Surrogacy: In this type of surrogacy, the surrogate mother uses her own egg, which is fertilized by the sperm of the intended father (or sperm donor). This means the surrogate mother is genetically related to the child.
- Gestational Surrogacy: In this type of surrogacy, the embryo is created using the eggs and sperm of the intended parents (or donors) and implanted into the surrogate mother. The surrogate is not genetically related to the child.
Since the Surrogacy (Regulation) Act 2021, gestational surrogacy has been the only legal form of surrogacy in India. The law strictly prohibits commercial surrogacy and limits surrogacy to altruistic arrangements where the surrogate is not financially compensated beyond medical expenses.
Latest surrogacy laws in India
The Surrogacy (Regulation) Act 2021, which was passed to curb commercial surrogacy and ensure the protection of surrogate mothers and children, includes specific guidelines about who can avail of surrogacy services in India. Under this law, only heterosexual married couples are legally eligible to pursue surrogacy, with some exceptions.

THE SURROGACY (REGULATION) ACT, 2021
- Altruistic Surrogacy only (no direct financial benefit to the surrogate mother)
- Registered Surrogacy Clinic only (ART Registered clinics can perform surrogacy).
- Single woman (divorced or widowed), between the age of 35 to 45 years. A genetic link is a must.
- Married Indian female (25 to 50 years) and male (26 to 55 years).
- Only Indian citizens and OCI are allowed to do surrogacy ( married couples)
- Couple have not had any healthy surviving child biologically or by adoption.
- Have to have Medical indication necessitating gestation surrogacy.
- To obtain a certificate of essentiality from The Appropriate Authority.
- To obtain certificate of medical indication necessitating gestation surrogacy from District Medical Board.
- Parentage Order passed by First class Magistrate.
- Surrogate Mother to obtain eligibility certificate from The Appropriate Authority.
- Surrogacy (Regulation) Amendment Rules, 2024- As of 21st Feb 2024, it is possible to use an egg donor or sperm donor if all other conditions are met.
Legal Framework of Surrogacy in India
The Indian government implemented the Surrogacy (Regulation) Act 2021 to regulate the surrogacy process and ensure the protection of both the surrogate mother and the child. Some key provisions of this law include:
- Eligibility: Surrogacy is only allowed for heterosexual married couples who have been married for at least five years and have proven infertility. It is not allowed for single individuals, same-sex couples, or live-in partners.
- Age Limits: The surrogate mother must be between the ages of 25 and 35, and the intended mother should be between 23 and 50 years of age. The intended father should be between 26 and 55 years of age.
- Altruistic Surrogacy: Surrogacy is only allowed on an altruistic basis, meaning the surrogate cannot be paid beyond her medical expenses and compensation for her loss of wages during the pregnancy.
- Ban on Commercial Surrogacy: Commercial surrogacy, where a woman is paid a fee for carrying a baby, is banned. This law aims to eliminate the exploitation of surrogates.
- Medical Guidelines: Surrogates must undergo medical and psychological assessments to ensure they are fit for the process and willing to participate.
The Surrogacy Process in India
The surrogacy process in India involves several steps, from initial consultations to the birth of the baby. Here’s a step-by-step overview of how surrogacy works in India:
1. Initial Consultation and Screening
The first step in the surrogacy process is to meet with a fertility specialist or surrogacy agency to discuss your options, requirements, and the legalities involved. Intended parents will undergo fertility assessments, including tests to determine their reproductive health. The surrogate mother is also screened for medical and psychological fitness. This ensures that she is physically capable of carrying the pregnancy and is emotionally prepared for the process.
- Psychological Screening: Surrogates are thoroughly screened to ensure that they understand the emotional and physical demands of pregnancy and surrogacy.
- Medical Screening: Surrogates undergo various health checks to ensure they are physically capable of carrying a pregnancy.
2. Choosing a Surrogate
Once the intended parents have been cleared for surrogacy, they must choose a surrogate mother. In India, surrogates are typically recruited through surrogacy agencies, which help find women who are willing to become surrogates. The surrogate is usually a married woman who already has children, as this demonstrates her ability to carry a pregnancy to term.
In the case of altruistic surrogacy, the surrogate may be a family member or someone from the surrogate’s community. The surrogate mother’s agreement is critical to the process, as it outlines her responsibilities and compensation for medical expenses.
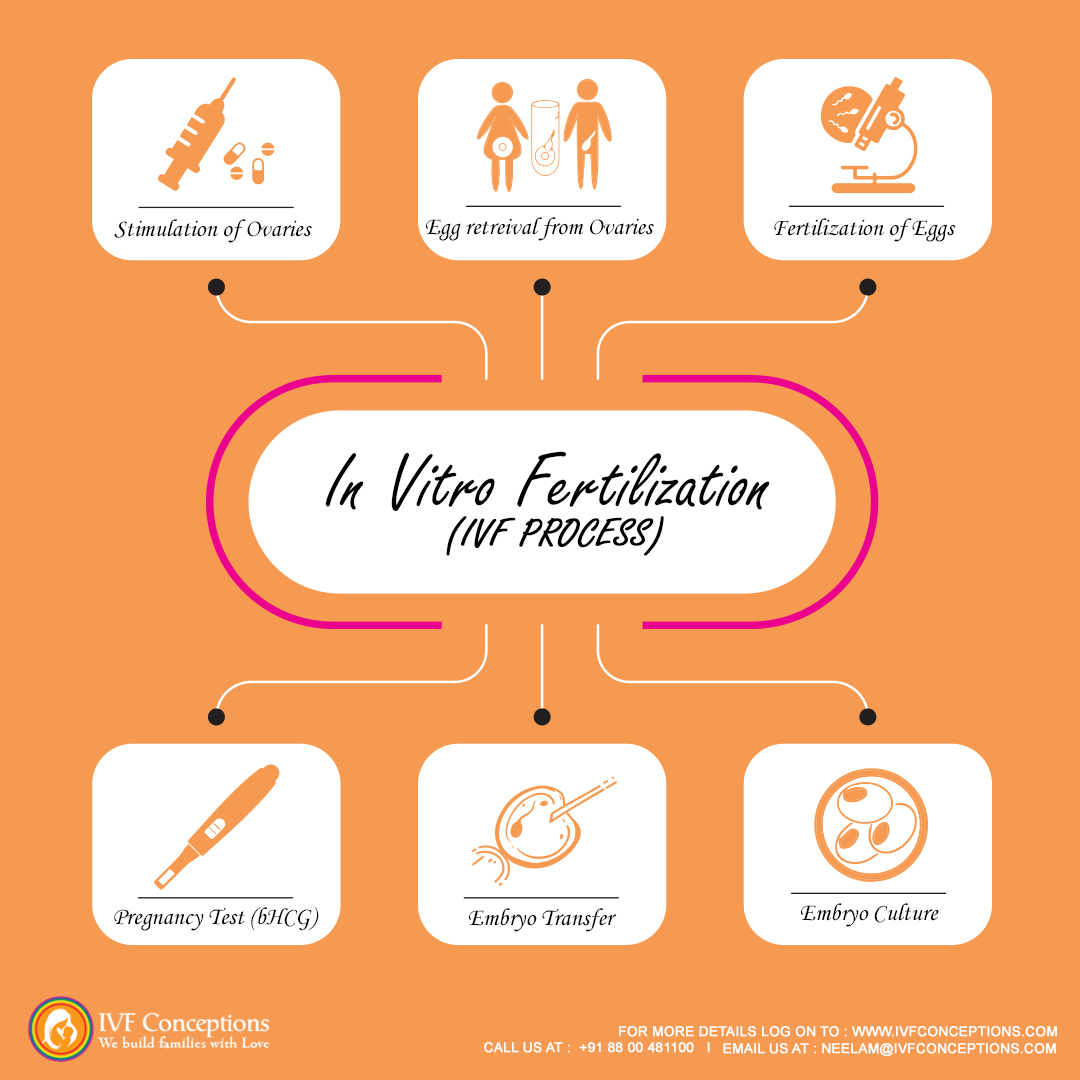
3. In Vitro Fertilization (IVF)
Once a suitable surrogate is selected, the next step involves in vitro fertilization (IVF). The process involves the following:
- Egg Retrieval: If the intended mother is providing the eggs, they are retrieved through a minor surgical procedure. Alternatively, eggs from an egg donor can be used.
- Sperm Collection: The sperm of the intended father (or sperm donor) is collected for fertilization.
- Embryo Creation: The eggs are fertilized with the sperm in the lab to create embryos.
- Embryo Transfer: Once the embryos are ready, they are implanted into the surrogate mother’s uterus, using a procedure called embryo transfer. This is a critical step, and not all transfers result in pregnancy.
4. Pregnancy and Monitoring
After embryo transfer, the surrogate mother is monitored closely to ensure the pregnancy is progressing well. She will undergo regular checkups, including ultrasounds, to monitor the baby’s growth and health. Medical support is provided throughout the pregnancy to ensure the surrogate’s well-being.
The surrogate mother is also given medications to support the pregnancy and prevent premature labor. All medical expenses, including hospital visits and medication, are covered by the intended parents.
5. Childbirth and Legal Proceedings
Once the pregnancy reaches full term, the surrogate mother will give birth to the baby. After the birth, the intended parents will legally become the parents of the child. In India, the birth certificate will list the intended parents as the legal parents, and the surrogate mother will have no parental rights over the child.
In order to finalize the surrogacy arrangement, intended parents must complete the legal formalities, including:
- Parental Rights: The intended parents will need to obtain a parental order or court order to establish their legal rights over the child.
- Surrogate’s Compensation: The surrogate mother will be compensated for her medical expenses, as well as any lost wages during the pregnancy. However, any payment beyond this is prohibited by law.
More Resources to Read:
Surrogacy Process Explained for Intended Parents
How Long Does the Surrogacy Process Take?
Top 5 Things To Know Before Going For Surrogacy Process
Finding the Best IVF Clinic in India: Expert Guide
Conclusion
Surrogacy in India is a highly regulated process, aimed at ensuring the protection and welfare of both the surrogate mother and the child. Since the passing of the Surrogacy (Regulation) Act 2021, commercial surrogacy is banned, and surrogacy is only allowed on an altruistic basis. Intended parents must meet specific eligibility requirements, and the surrogate mother undergoes rigorous medical and psychological screening.
The surrogacy process in India is comprehensive, involving IVF, medical support, and legal procedures to ensure that both the intended parents and the surrogate mother are protected throughout the journey. Whether you are an Indian or international intended parent, it is important to work with a reputable surrogacy agency or fertility clinic to guide you through the complex process.
If you are considering surrogacy in India, always consult with a legal expert and a qualified medical professional to understand the legal implications and ensure the process is carried out ethically and legally.
We are leading International Surrogacy Industry Expert with more than 15 years of global experience and expertise. Get in touch with us about affordable, reliable, and legal surrogacy options.
We are leading International Surrogacy Industry Expert with more than 15 years of global experience and expertise. Get in touch with us about affordable, reliable, and legal surrogacy options.
If you’d like to learn more about IVF, Egg Donation, or surrogacy services globally, check out the rest of our website at Georgia Surrogacy Agency. We offer legally secure and affordable surrogacy consulting services for FREE.
Get in touch for FREE SURROGACY CONSULTING:
Mobile: +91-8800481100 ( WhatsApp, Line, Viber)
Email: neelam@ivfconceptions.com
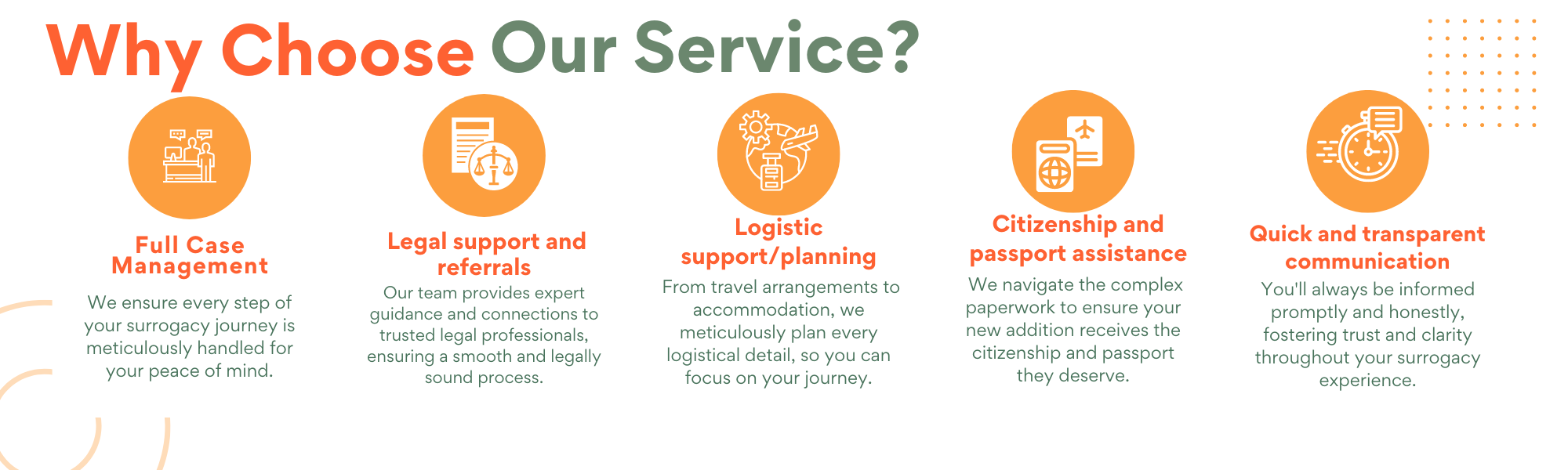
Why Choose us for your smooth and successful surrogacy journey!!
- Option of choosing multiple surrogacy destinations with 14+ Years of international surrogacy experience.
- Getting a chance to work with fertility clinics/agencies that are elite and have proven track record with reference from existing IPs.
- Option of choosing multiple egg donor options- Asian, Caucasian, African, Oriental etc.
- All transparent financial transactions with affordability. You make direct payment with no additional fee on top.
- No hidden agent fee or surprise cost later on. All fees paid directly as per the agreement signed with service provider.
- Dedicated case manager to each IPs.
- Honest, transparent and quick communications.
- Assistance in all legal matters pertaining to visa and taking baby home process.
- Local support with access to all medical reports of egg donors and surrogate mothers.
- Assistance in all logistics of frozen sperms/embryos shipments.
- Last but not least, we have years of experience in coordinating delicate surrogacy programs with great personal care.
FAQs About Surrogacy in India
1. Is surrogacy legal in India?
Yes, surrogacy is legal in India. However, it is regulated by the Surrogacy (Regulation) Act 2021, which permits gestational surrogacy only on an altruistic basis. Commercial surrogacy, where the surrogate receives payment beyond medical expenses, is prohibited.
2. Is commercial surrogacy allowed in India?
No, commercial surrogacy is banned in India. The Surrogacy (Regulation) Act 2021 restricts surrogacy to altruistic arrangements, meaning surrogates can only receive compensation for medical expenses and any lost wages during pregnancy, but no additional fees.
3. Who can opt for surrogacy in India?
Surrogacy in India is available to heterosexual married couples who have been married for at least five years and are unable to conceive. They must also prove infertility. Single men, women, and same-sex couples are not eligible under the current law.
4. What is the age limit for surrogacy in India?
The surrogate mother must be between 25 and 35 years of age. The intended mother should be between 23 and 50 years of age, and the intended father should be between 26 and 55 years of age.
5. What is the surrogacy process in India?
The surrogacy process in India typically involves IVF (in vitro fertilization), where embryos are created using the intended parents’ eggs and sperm (or donors). These embryos are then implanted into the surrogate mother. The surrogate undergoes regular medical checkups and delivers the child, after which the intended parents are legally recognized as the parents.
6. Is surrogacy allowed for single parents in India?
No, under the Surrogacy (Regulation) Act 2021, surrogacy is not permitted for single individuals. Only heterosexual married couples with proven infertility are eligible for surrogacy in India.
7. What is altruistic surrogacy in India?
Altruistic surrogacy refers to a surrogacy arrangement where the surrogate mother does not receive any financial compensation beyond medical expenses and reimbursement for lost wages during the pregnancy. She carries the child for the intended parents without any monetary gain.
8. How much does surrogacy cost in India?
The cost of surrogacy in India generally ranges between INR 20L to INR 30L based on the services you need, location of the fertility clinics, experience of the fertility doctor.
This includes medical expenses, surrogate compensation, legal fees, and other associated costs. However, prices can vary depending on the fertility clinic, location, and specific circumstances of the surrogacy.
9. Are there any legal issues associated with surrogacy in India?
Yes, there are several legal considerations when it comes to surrogacy in India. These include obtaining parental rights for the intended parents, ensuring the surrogate’s consent, and following the proper legal procedures. It’s important to work with a legal expert to navigate these issues.
10. What happens if the surrogate mother changes her mind?
The surrogate mother must sign a legally binding contract agreeing to carry the child for the intended parents. This contract ensures that the surrogate cannot change her mind once she has agreed to the arrangement. However, if the surrogate mother has valid reasons to not proceed, the intended parents and legal authorities will be involved to address the issue in a lawful manner.
11. Can a surrogate mother keep the child in India?
No, under Indian law, the surrogate mother has no legal rights to the child after birth. The intended parents are legally recognized as the parents once the birth is registered, and the surrogate has no claim over the child.
12. Are there any psychological screening requirements for surrogates?
Yes, as per the Surrogacy (Regulation) Act 2021, surrogates must undergo psychological screening to ensure they are emotionally prepared for the process. This helps prevent any emotional distress for the surrogate during the pregnancy.
13. How do intended parents obtain legal parentage in surrogacy?
After the child is born, the intended parents must complete the legal formalities to establish their parental rights. They need to obtain a parental order or court order to be legally recognized as the parents. This ensures that the intended parents’ names are on the birth certificate.
14. Can a foreign couple opt for surrogacy in India?
Yes, international intended parents can pursue surrogacy in India, provided they meet the eligibility criteria specified by the Indian government. However, foreign couples must ensure they comply with the specific legal regulations for surrogacy, including obtaining the necessary permissions and paperwork.

Highly esteemed, authoritative, and trusted professional with a 14-year of experience in international surrogacy. Advocate for Secure, Legal, and Affordable International Surrogacy.
Neelam Chhagani, MA (Counselling Psychology) and Holistic Infertility and Third-Party Reproduction Consultant.
Member of European Fertility Society, Best Surrogacy Blogger of 2020, with 300 dedicated blogs, and top contributor on Quora for Surrogacy.


Add Your Comment