Complete Surrogacy Guide for Parents: Types, Process, Costs, Risks, Techniques, and Legislation
Surrogacy is a complex and rewarding journey for those looking to expand their families. This guide provides an in-depth look at the surrogacy process, types, legal aspects, and more, offering a comprehensive resource for intended parents.
- Book an online appointment: Get a free online consultation.
- Call\W:+91-8800481100 Email:neelam@ivfconceptions.com
Who Can Opt for Surrogacy?
Surrogacy is a viable option for various individuals and couples:
- Same-Sex Couples: Often, gay couples use surrogacy to have a genetically related child.
- Single Parents: Surrogacy allows single men or women to become parents without the need for a partner.
- Individuals with Medical Issues: Conditions such as uterine problems, severe diabetes, heart disease, or a history of pregnancy complications can make surrogacy a preferable option.
Additional Guides for Surrogacy in Georgia
How to find surrogate mother in Argentina
How to find surrogate mother in Georgia
Selecting a Surrogate Mother

Choosing a surrogate is a critical step, and specific criteria should be met:
| Criteria | Details |
| Age | 21-45 years (some agencies may have different requirements). |
| Health | No history of major pregnancy complications, postpartum depression, or untreated STDs. |
| Lifestyle | No smoking, drinking, and must have a BMI of less than 30. |
| Previous Pregnancy | Must have at least one successful pregnancy and be raising her own child. |
| Psychological Stability | Must have discontinued any antidepressants or anti-anxiety medication at least 12 months prior. |
| Travel | Must be willing to travel for appointments if necessary. |
Pros and Cons of Surrogacy
Pros
- Creates Relationships: Surrogacy often leads to lasting bonds between the surrogate and the intended parents.
- Completes Families: Surrogacy allows families, including those in the LGBTQ+ community, to have children.
- Involvement: Intended parents can be actively involved in the pregnancy process, including attending appointments and milestone events.
- High Success Rates: Surrogacy, especially gestational surrogacy, has a high success rate.
Cons
- Complications: Legal and medical complications can arise, making the process complex.
- Cost: Surrogacy can be expensive, requiring significant financial resources.
- Time Consumption: The process, including the nine-month pregnancy, is time-intensive.
- Emotional Demands: Surrogacy can be emotionally challenging, particularly for the surrogate who must part with the baby.
Surrogacy: Types, Complications, and Techniques
Types of Surrogacy
- Traditional Surrogacy: The surrogate uses her own eggs, making her the biological mother.
- Gestational Surrogacy: The surrogate has no genetic link to the child, as the embryo is created using the intended parents’ or donors’ eggs and sperm.
Other forms include:
- Commercial Surrogacy: The surrogate receives financial compensation.
- Altruistic Surrogacy: The surrogate is not paid but may be reimbursed for expenses.
Complications in Surrogacy
| Type of Complication | Details |
| Legal Complications | Contracts must cover all potential outcomes and responsibilities. Surrogacy laws vary by country and state, requiring careful legal planning. |
| Medical Complications | Risks include multiple pregnancies, preeclampsia, gestational diabetes, and more. Obstetrical complications are more common in surrogacy compared to typical pregnancies. |
Techniques Used in Surrogacy
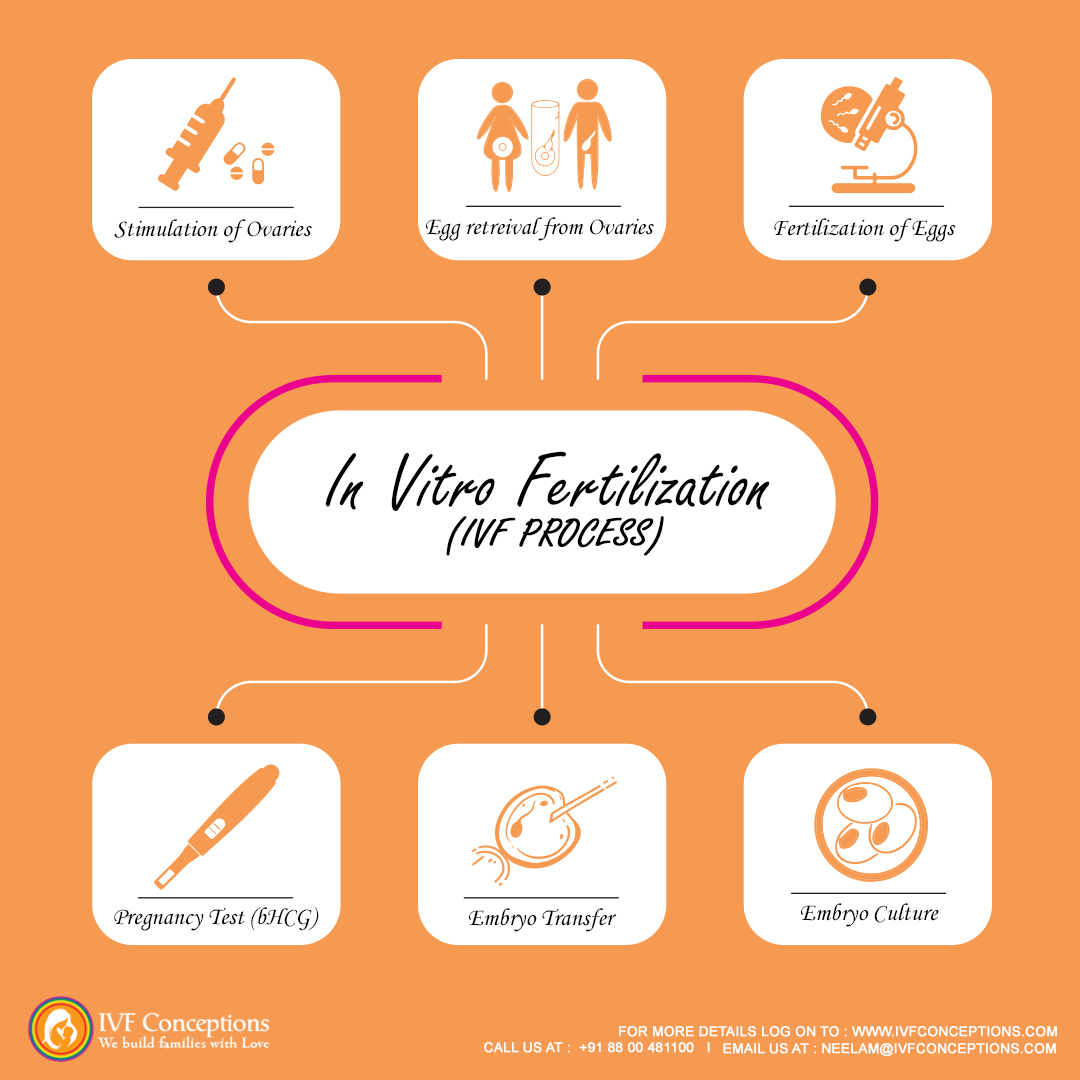
- IUI (Intrauterine Insemination): A less invasive and less expensive fertility treatment where sperm is placed directly into the uterus.
- IVF (In Vitro Fertilization): A complex process where eggs are fertilized outside the body and then transferred to the uterus. IVF is more commonly used in gestational surrogacy.
Step-by-Step Process of Surrogacy: Types, Surrogacy Pros, and Cons
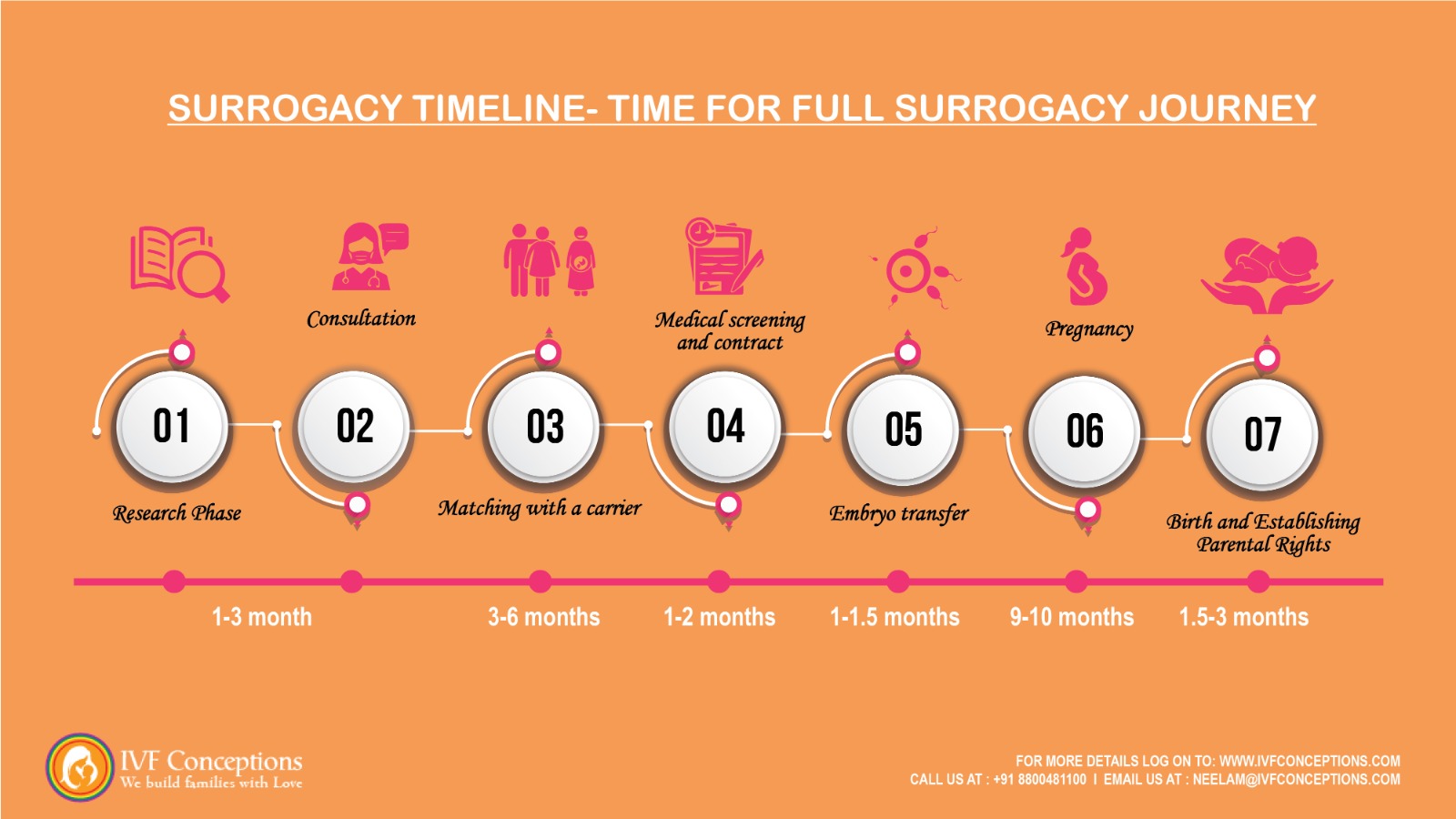
The surrogacy process takes 18 months to 24 months depending upon the individual circumstances
Outlines the surrogacy process timeline for intended parents:
| Stage | Description of Stage | Duration |
| Research Phase | Explore family building options and decide on surrogacy. | Personal timeframe |
| Consultation and Application | Choose a surrogacy agency, sign agreement, and start embryo creation (if needed). | 1-3 Months |
| Matching | Agency finds and presents potential gestational carriers. Meet and decide on a match. | 3-6 Months |
| Medical Screening and Contracts | Carrier undergoes medical and psychological screening. Sign surrogacy contract. | 1-2 Months |
| Embryo Transfer | Prepare for embryo transfer. Success may take multiple attempts. | 1-1.5 Months |
| Pregnancy | Gestational carrier’s pregnancy, approximately 40 weeks. | 9-10 Months |
| Birth and Postpartum | Baby’s birth, establish parental rights, and postpartum period. | 1.5-3 Months |
Please keep in mind that the durations mentioned in the table are approximate and can vary depending on individual circumstances and other factors. Always consult with a reputable surrogacy agency or professional to get personalized guidance throughout the surrogacy journey.
1) Decide Whether Surrogacy is the Right Choice
The first and most crucial step in any surrogacy journey is determining if it’s the right path for you. Surrogacy is both a financial and emotional commitment, requiring careful consideration. Discuss with your partner or family the potential pros and cons, and consult with medical and legal professionals to ensure that surrogacy aligns with your family goals.
2) Preparing for Surrogacy
After deciding on surrogacy, the next step is preparing for the journey. This involves selecting the type of surrogacy:
- Traditional Surrogacy: The surrogate uses her own eggs and is artificially inseminated with the intended father’s or donor’s sperm.
- Gestational Surrogacy: The surrogate carries an embryo created using the egg of the intended mother or donor and sperm from the intended father or donor.
You will also need to decide whether to work with a surrogacy agency or a surrogacy attorney:
| Surrogacy Option | Description |
| Surrogacy Agency | Provides full services, including screening, matching, legal, and medical support. |
| Surrogacy Attorney | Handles the legal aspects, such as contracts and citizenship documentation, but may not provide other services. |
3) Matching with the Surrogate
Finding the right surrogate is critical to a successful surrogacy journey. Surrogacy agencies typically facilitate this process by matching intended parents with surrogates who have similar goals and expectations. Once a match is found, the parties can get to know each other through meetings and discussions before formalizing the match with a legal contract.
4) Drawing the Legal Contract
Legal contracts are essential to protect the rights of both the intended parents and the surrogate. Each party should have independent legal counsel to review and negotiate the terms. Once all parties agree, the contract is signed, and the surrogacy process moves forward.
5) Fertilization and Embryo Transfer Process
The medical aspect of surrogacy begins with the IVF process. The intended mother or egg donor undergoes ovarian stimulation to produce eggs, which are then retrieved and fertilized with sperm from the intended father or donor. The resulting embryos are transferred to the surrogate’s uterus. Upon confirmation of pregnancy, the surrogate begins receiving payments for expenses and base compensation.
6) Welcoming the Child
After the birth, the child is handed over to the intended parents, and both the surrogate and the new family can choose to maintain a relationship. The legal parentage is established, and the surrogate’s role concludes, allowing the intended parents to enjoy their new family.
The Surrogacy Process Stages
The surrogacy process can be divided into three main stages:
| Stage | Description |
| Egg Donation | Retrieval of eggs from the intended mother or donor, followed by fertilization with the intended father’s sperm. |
| Fertilization | The fertilized eggs (embryos) are cultured and monitored for development before being transferred to the surrogate. |
| Embryo Transfer | Transfer of the embryo(s) into the surrogate’s uterus, where the pregnancy begins. |
Additional Resources to Read:
How to find surrogate mother in USA
Why is Surrogacy in Georgia the Right option for childless couples in the USA or Europe?
Top Countries for Surrogacy: A Comprehensive Guide for Intended Parents
What Are the International Surrogacy Laws by Country?
Surrogacy laws vary significantly across the globe, with some countries offering more favorable conditions for surrogacy than others.
| Country | Surrogacy Laws |
| Australia | Only altruistic surrogacy is allowed; commercial surrogacy is prohibited. |
| Canada | Commercial surrogacy is illegal, but altruistic surrogacy is allowed with reimbursement for reasonable expenses. |
| Greece | Altruistic surrogacy is legal for both Greek citizens and foreign nationals. Only opposite-sex couples and single women are eligible. |
| USA | Both altruistic and commercial surrogacy are legal, but laws vary by state. Some states are surrogacy-friendly, while others have restrictive or no surrogacy laws. |
| Ukraine | Gestational surrogacy is legal and well-regulated, making it a popular destination for international intended parents. |
| Russia | Surrogacy is legal for heterosexual couples and single women, including foreign nationals, but limited to gestational surrogacy arrangements. |
| South Africa | Only altruistic surrogacy is allowed, and agreements must be confirmed by the High Court. Commercial surrogacy is prohibited. |
If you’d like to learn more about IVF, Egg Donation, or surrogacy services globally, check out the rest of our website at Georgia Surrogacy Agency. We offer legally secure and affordable surrogacy consulting services for FREE.
Get in touch for FREE SURROGACY CONSULTING:
Mobile: +91-8800481100 ( WhatsApp, Line, Viber)
Email: neelam@ivfconceptions.com
FAQs About Surrogacy
Q1: What is the difference between traditional and gestational surrogacy?
A1: Traditional surrogacy involves the surrogate’s own egg, making her the biological mother, whereas in gestational surrogacy, the surrogate carries an embryo with no genetic link to her.
Q2: How much does surrogacy cost?
A2: The cost of surrogacy varies widely depending on the country, type of surrogacy, and whether you use an agency. In the U.S., costs can range from $90,000 to $150,000.
Q3: Is surrogacy legal everywhere?
A3: No, surrogacy laws vary by country and even within countries. Some places fully legal

Highly esteemed, authoritative, and trusted professional with a 14-year of experience in international surrogacy. Advocate for Secure, Legal, and Affordable International Surrogacy.
Neelam Chhagani, MA (Counselling Psychology) and Holistic Infertility and Third-Party Reproduction Consultant.
Member of European Fertility Society, Best Surrogacy Blogger of 2020, with 300 dedicated blogs, and top contributor on Quora for Surrogacy.


Add Your Comment