Surrogacy in Canada
Surrogacy in Canda is possible but only altruistic surrogacy arrangements. Surrogacy is a remarkable journey that allows individuals and couples to fulfill their dreams of starting or expanding their families. In Canada, surrogacy has emerged as a viable and increasingly sought-after option for those facing infertility challenges or other medical conditions that make traditional pregnancy difficult or impossible.
- Book an online appointment: Get a free online consultation.
- Call\W:+91-8800481100 Email:neelam@ivfconceptions.com
The decision to pursue surrogacy is a deeply personal and emotional one, and Canada has established a legal framework that aims to support and protect the rights and well-being of all parties involved, including intended parents, surrogates, and the children born through surrogacy arrangements.
Additional Guides to Read:
How to find surrogate mother in Argentina
How to find surrogate mother in Georgia
Over the past decade, the demand for surrogacy in Canada has grown significantly but still not very popular due to its outdates laws and due to altruistic nature of surrogacy with long waiting list for gestational surrogate mother in Canada. This can be attributed to several factors, including:
- Advancements in reproductive technologies and increased awareness of surrogacy as a family-building option.
- Legal recognition and regulation of surrogacy agreements, providing a clear and secure process for intended parents and surrogates.
- A commitment to ethical practices and the well-being of all parties involved, particularly the children born through surrogacy.
As more Canadians explore surrogacy as a path to parenthood, it’s crucial to understand the legal and ethical considerations, the various types of surrogacy arrangements, and the step-by-step process involved. In this blog post, we’ll delve into the intricacies of surrogacy in Canada, providing you with valuable insights and information to help you navigate this journey successfully.
Key Points:
- Surrogacy is a family-building option for individuals and couples facing infertility challenges or medical conditions.
- Canada has a legal framework that aims to support and protect the rights and well-being of all parties involved in surrogacy arrangements.
- The demand for surrogacy in Canada has grown significantly in recent years due to various factors, including advancements in reproductive technologies and legal recognition of surrogacy agreements.
Is Surrogacy Legal in Canada?
Surrogacy is legal in Canada, but it is subject to specific regulations and requirements to ensure the safety and well-being of all parties involved, particularly the children born through surrogacy arrangements.
The legal framework surrounding surrogacy in Canada is governed by the Assisted Human Reproduction Act (AHRA), which was introduced in 2004. This act outlines the following key principles:
- Altruistic Surrogacy Only: In Canada, only altruistic (non-commercial) surrogacy arrangements are permitted. This means that surrogate mothers cannot be compensated beyond reimbursement for approved expenses related to the surrogacy process, such as medical expenses, legal fees, and potential loss of income.
- No Commercial Trade: The buying and selling of human eggs, sperm, embryos, or surrogacy services is prohibited under Canadian law. This is to prevent the commercialization of reproductive materials and services.
- Pre-Birth Parentage Orders: Intended parents can obtain a pre-birth parentage order from the court, which establishes their legal parentage of the child before birth. This order helps ensure a smooth transition of parental rights and responsibilities after the child’s birth.
Requirements for Intended Parents:
- Undergo medical and psychological evaluations
- Provide evidence of infertility or medical need for surrogacy
- Demonstrate the ability to support and care for the child
Requirements for Surrogate Mothers:
- Be at least 21 years old
- Have previously given birth
- Undergo medical and psychological evaluations
- Obtain independent legal advice
- Provide informed consent
It’s important to note that surrogacy laws and regulations can vary slightly across different provinces and territories in Canada. Additionally, the legal landscape surrounding surrogacy is constantly evolving, with recent debates and discussions around potential changes to the AHRA.
Intended parents and surrogate mothers are strongly advised to seek legal counsel and work with experienced surrogacy professionals to ensure full compliance with all applicable laws and regulations throughout the surrogacy process.
Key Points:
- Surrogacy is legal in Canada, but only altruistic (non-commercial) arrangements are permitted.
- The Assisted Human Reproduction Act (AHRA) governs surrogacy regulations and prohibits the buying and selling of reproductive materials and services.
- Intended parents and surrogate mothers must meet specific requirements and undergo evaluations.
Cost of Surrogacy in Canada
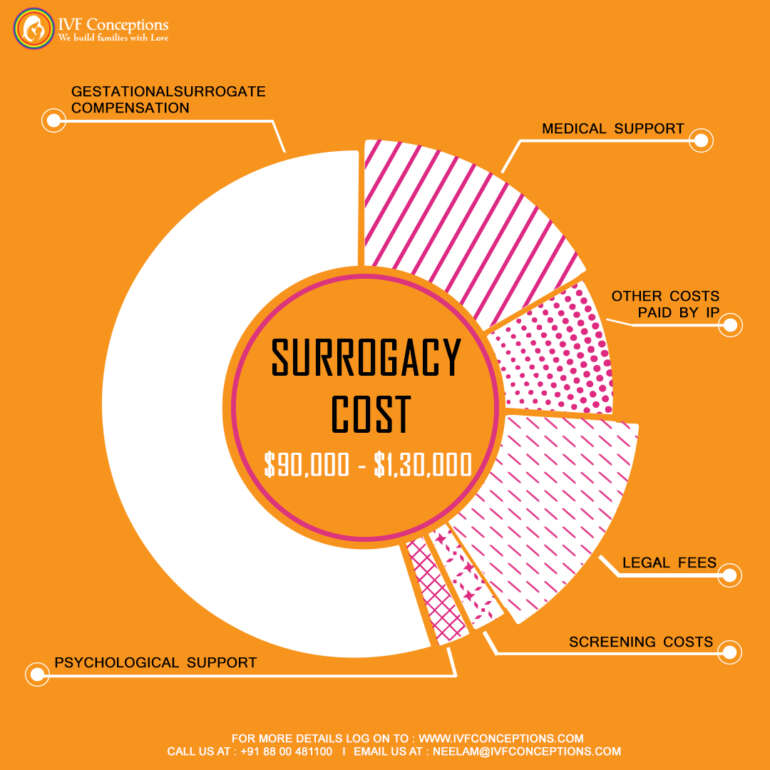
surrogacy in Canada cost in the range of $80,000 to $100,000.
While surrogacy in Canada is governed by altruistic principles, meaning surrogate mothers cannot be compensated beyond reimbursement for approved expenses, the overall process can still be financially significant for intended parents. The costs associated with surrogacy in Canada can vary depending on several factors, including medical procedures required, legal fees, and potential travel expenses.
Typical expenses involved in surrogacy in Canada may include:
- Medical Expenses:
- In Vitro Fertilization (IVF) treatments
- Fertility medications
- Embryo transfer procedures
- Prenatal care and delivery costs for the surrogate
- Legal Fees:
- Drafting and reviewing surrogacy contracts
- Obtaining pre-birth parentage orders
- Legal representation for intended parents and surrogate
- Surrogate Reimbursements:
- Medical expenses (e.g., insurance premiums, co-pays)
- Potential loss of income during pregnancy and recovery
- Counseling and legal advice
- Travel and accommodation costs (if applicable)
- Agency Fees (if using a surrogacy agency):
- Surrogate screening and matching services
- Case management and coordination
- Counseling and support services
- Additional Expenses:
- Travel and accommodation costs for intended parents (if the surrogate lives in a different location)
- Counseling and support services for intended parents
To estimate the overall cost of surrogacy in Canada for your specific case, it’s advisable to consult with experienced surrogacy professionals, such as fertility clinics, lawyers, and surrogacy agencies. They can provide guidance and help you develop a comprehensive financial plan based on your unique situation.
Price of surrogacy in Canada
| Surrogacy Cost Item | Estimated Range |
|---|---|
| Medical Expenses | |
| In Vitro Fertilization (IVF) | $10,000 – $20,000+ |
| Fertility Medications | $3,000 – $8,000 |
| Embryo Transfer | $2,000 – $5,000 |
| Prenatal Care and Delivery | $5,000 – $15,000 |
| Legal Fees | |
| Surrogacy Contract | $3,000 – $8,000 |
| Pre-birth Parentage Order | $2,000 – $5,000 |
| Legal Representation | $5,000 – $15,000 |
| Surrogate Reimbursements | |
| Medical Expenses | $2,000 – $10,000 |
| Lost Income | $5,000 – $20,000 |
| Counseling and Legal Advice | $2,000 – $5,000 |
| Travel and Accommodation | $1,000 – $10,000+ |
| Agency Fees (if using an agency) | $10,000 – $30,000+ |
| Additional Expenses | |
| Intended Parents’ Travel and Accommodation | $2,000 – $15,000+ |
| Counseling and Support Services | $1,000 – $5,000 |
Please note that these are approximate ranges, and the actual costs may vary significantly based on individual circumstances, location, and the specific requirements of each surrogacy arrangement. It’s advisable to consult with surrogacy professionals and develop a detailed financial plan based on your unique situation.
Key Points:
- Surrogacy in Canada involves various expenses, including medical procedures, legal fees, and reimbursements for the surrogate’s approved expenses.
- Costs can vary significantly depending on factors such as medical complexity, travel requirements, and the use of surrogacy agencies.
- Consulting with surrogacy professionals and creating a detailed financial plan is essential for budgeting and preparing for the associated costs.
Pros and Cons of Surrogacy in Canada
While surrogacy offers a pathway to parenthood for many individuals and couples in Canada, it’s essential to carefully consider both the advantages and potential challenges before embarking on this journey. By weighing the pros and cons, you can make an informed decision that aligns with your needs, values, and emotional well-being.
Pros of Surrogacy in Canada:
- Legal Framework and Protections:
- Canada has a well-established legal framework that regulates surrogacy arrangements and provides clear guidelines for all parties involved.
- Pre-birth parentage orders ensure a smooth transition of parental rights and responsibilities.
- Availability of Reputable Clinics and Professionals:
- Canada is home to numerous reputable fertility clinics and experienced medical professionals specializing in assisted reproductive technologies and surrogacy.
- Access to high-quality medical care and support throughout the surrogacy process.
- Ethical and Altruistic Approach:
- Surrogacy in Canada is based on altruistic principles, minimizing the risk of exploitation and commercialization.
- Surrogate mothers are motivated by a desire to help others build families, rather than financial incentives.
- Support and Counseling Services:
- Many surrogacy agencies and clinics in Canada offer counseling and support services for intended parents, surrogates, and their families, addressing emotional and psychological needs.
Cons of Surrogacy in Canada:
- Limited Availability of Surrogates:
- Due to the altruistic nature of surrogacy in Canada, there may be a limited pool of available surrogates, potentially leading to longer wait times for intended parents.
- Lengthy Legal Process:
- Obtaining pre-birth parentage orders and navigating the legal requirements can be a time-consuming and complex process, requiring patience and legal guidance.
- Financial Considerations:
- While commercial surrogacy is prohibited, the medical procedures, legal fees, and reimbursements for the surrogate’s expenses can add up, making surrogacy a significant financial investment.
- Emotional and Ethical Concerns:
- Surrogacy can raise emotional and ethical concerns, such as the potential for attachment issues, feelings of loss for the surrogate, or concerns about the child’s well-being and identity.
- Ongoing counseling and open communication are essential to address these concerns.
- Geographical Challenges:
- If the intended parents and surrogate reside in different provinces or territories, additional logistical and travel arrangements may be required, adding to the complexity and costs.
| Pros | Cons |
|---|---|
| Legal framework and protections | Limited availability of surrogates |
| Availability of reputable clinics and professionals | Lengthy legal process |
| Ethical and altruistic approach | Financial considerations |
| Support and counseling services | Emotional and ethical concerns |
| Geographical challenges |
More Resources to Read:
What are the Starting Steps for Surrogacy Process in Georgia?
How Much Does Surrogacy Cost in Georgia Country
Surrogacy for Hetero Couples in Georgia Europe
Gay Surrogacy in Canada
Canada’s surrogacy laws and regulations are inclusive and non-discriminatory, providing equal opportunities for same-sex couples and individuals, regardless of their sexual orientation or gender identity, to pursue surrogacy as a path to parenthood.
Rights and Options for Gay Couples and Individuals:
- Equal Access to Surrogacy Services:
-
-
- Gay couples and individuals have the same rights and access to surrogacy services as heterosexual couples in Canada.
- Surrogacy agencies, fertility clinics, and professionals cannot discriminate based on sexual orientation or gender identity.
-
- Legal Parentage Recognition:
-
-
- Through pre-birth parentage orders, gay couples and individuals can establish their legal parentage of the child born through surrogacy, ensuring their parental rights and responsibilities are recognized from birth.
-
- Use of Donor Eggs or Sperm:
-
-
- Gay couples and individuals may choose to use donor eggs or sperm in their surrogacy journey, allowing them to have a genetic connection to the child.
- Reputable fertility clinics and sperm banks in Canada offer donor services and follow strict screening protocols.
-
- Option for Co-Parenting Arrangements:
-
- In some cases, gay couples or individuals may choose to co-parent with another individual or couple, creating a shared parenting arrangement.
- Legal agreements and counseling are recommended to ensure clear expectations and responsibilities.
Considerations and Resources:
- LGBTQ+ Inclusive Surrogacy Agencies and Professionals:
- Many surrogacy agencies and professionals in Canada are well-versed in working with LGBTQ+ clients and understand their unique needs and concerns.
- Researching and selecting LGBTQ+-friendly agencies and professionals can ensure a supportive and inclusive experience.
- LGBTQ+ Support Networks:
- Various organizations and support groups exist in Canada to provide resources, guidance, and emotional support to LGBTQ+ individuals and couples pursuing surrogacy.
- These networks can offer valuable insights, connect individuals with others who have been through the process, and provide a sense of community.
- Counseling and Preparation:
- Seeking counseling and guidance can help LGBTQ+ individuals and couples prepare for the emotional, legal, and practical aspects of surrogacy, including addressing any potential challenges or concerns specific to their circumstances.
By ensuring equal access and non-discrimination, Canada’s surrogacy laws and regulations create an inclusive environment for the LGBTQ+ community to explore surrogacy as a means of building their families. With the right resources and support, gay couples and individuals can navigate the surrogacy process with confidence and achieve their dreams of parenthood.
Conclusion
Surrogacy in Canada offers a viable and legally recognized path to parenthood for individuals and couples facing infertility challenges or other medical conditions that make traditional pregnancy difficult or impossible. Throughout this blog post, we’ve explored the various aspects of surrogacy in Canada, including the legal framework, costs, pros and cons, and considerations for the LGBTQ+ community.
One of the key takeaways is the importance of understanding the legal and financial aspects of surrogacy in Canada. The Assisted Human Reproduction Act (AHRA) provides a clear regulatory framework, allowing only altruistic surrogacy arrangements and prohibiting the commercialization of reproductive materials and services. While surrogate mothers cannot be compensated beyond reimbursement for approved expenses, the overall process can still involve significant costs, including medical procedures, legal fees, and potential travel expenses.
Canada’s inclusive approach to surrogacy extends to the LGBTQ+ community, providing equal access and non-discrimination for same-sex couples and individuals who wish to pursue surrogacy. With the right resources and support networks, LGBTQ+ intended parents can navigate the surrogacy process with confidence and achieve their dreams of parenthood.
If you’d like to learn more about IVF, Egg Donation, or surrogacy services globally, check out the rest of our website at Georgia Surrogacy Agency. We offer legally secure and affordable surrogacy consulting services for FREE.
Our team has over 14 years of experience facilitating surrogacy arrangements, egg donation, and serving as an advocacy resource for infertile couples and LGBTQ individuals seeking to build families.
For more resources on IVF and Surrogacy, browse our other web page- IVF Conceptions.
For more resources on IVF and Surrogacy, browse our other web page- Complete Surrogacy.
More reference:
https://www.aljazeera.com/features/2023/9/6/georgia-plans-to-ban-commercial-surrogacy
https://ge.usembassy.gov/message-for-u-s-citizens-new-law-banning-surrogacy-planned-in-georgia/
FAQs for surrogacy in Canada
- What is the difference between traditional and gestational surrogacy?
Traditional surrogacy involves the surrogate mother being artificially inseminated with the intended father’s sperm, making her the biological mother of the child. In gestational surrogacy, the surrogate carries a child conceived through in vitro fertilization (IVF) using the intended parents’ or donor eggs and sperm, and she has no genetic connection to the child.
- Can same-sex couples pursue surrogacy in Canada?
Yes, Canada’s surrogacy laws are inclusive and non-discriminatory, allowing same-sex couples and individuals to access surrogacy services and establish legal parentage through pre-birth parentage orders.
- How long does the surrogacy process typically take in Canada?
The surrogacy process can take anywhere from 12 to 24 months or longer, depending on various factors such as finding a suitable surrogate match, completing the necessary medical procedures, and navigating the legal requirements.
- Can intended parents use donor eggs or sperm in their surrogacy journey?
Yes, intended parents can use donor eggs, sperm, or embryos in their surrogacy journey. Reputable fertility clinics and sperm banks in Canada offer donor services and follow strict screening protocols.
- Are there any residency requirements for intended parents in Canada?
While there are no specific residency requirements for intended parents, the laws and regulations surrounding surrogacy may vary slightly across different provinces and territories. It’s essential to understand the local laws where the surrogacy arrangement will take place.
- What legal protections are in place for surrogate mothers in Canada?
Surrogate mothers in Canada have their rights protected by the Assisted Human Reproduction Act (AHRA). They have the right to independent legal advice, counseling, and informed consent throughout the process. Additionally, surrogacy contracts are legally enforceable, ensuring their rights and responsibilities are clearly outlined.
- Can surrogates receive compensation beyond reimbursement for expenses in Canada?
No, under Canadian law, surrogates cannot be compensated beyond reimbursement for approved expenses related to the surrogacy process, such as medical expenses, legal fees, and potential loss of income. This is to prevent the commercialization of surrogacy.
- What happens if the intended parents or surrogate change their mind during the process?
If either party changes their mind during the surrogacy process, they should seek legal advice and counseling immediately. The well-being of the child and all parties involved should be the top priority, and open communication and adherence to legal agreements are essential.

Highly esteemed, authoritative, and trusted professional with a 14-year of experience in international surrogacy. Advocate for Secure, Legal, and Affordable International Surrogacy.
Neelam Chhagani, MA (Counselling Psychology) and Holistic Infertility and Third-Party Reproduction Consultant.
Member of European Fertility Society, Best Surrogacy Blogger of 2020, with 300 dedicated blogs, and top contributor on Quora for Surrogacy.


Add Your Comment